Why we need stress-test?
Stress testing is an essential activity to ensure smooth operations and performance by simulating load on a system or application to analyse its behaviour under high workloads. By carrying out these tests before the software/app goes into live services, it helps identify weak spots that may affect user satisfaction or cause failures due to excessive demands during peak periods. Hence stress test tools play an integral part in testing scenarios that would not normally be possible when operating at lower loads thereby giving us a head start towards ensuring successful performance optimisations prior release onto the market.
How to check DBMS?
One of the main component any system its DBMS, often we need to check work and give adequate mark of performance on the server. Many things depend on the configuration and hardware possibilities system, of course that always have to estimate in setup at all with software and hardware of server, in that article we consider only DBMS test.
First of all we need to update indexes and upgrade packages on the machine:
apt update && apt upgrade 
For stress-testing we will use sysbench which represents multi tool without requirements for complicated test, express way to estimate transaction and speed DBMS. Next we download and install package from repository:
apt install sysbench
We will use OLTP way for test, that mean Online Transaction Processing literally and in the process represent simultaneously processing data from multiply users. That system appropriate for short and often transactions, for write and read! Next we need to make preparation for test, login into the DBMS by the privilege user, for example root and create DB:
SHOW DATABASES;And now create data base:
CREATE DATABASE gg;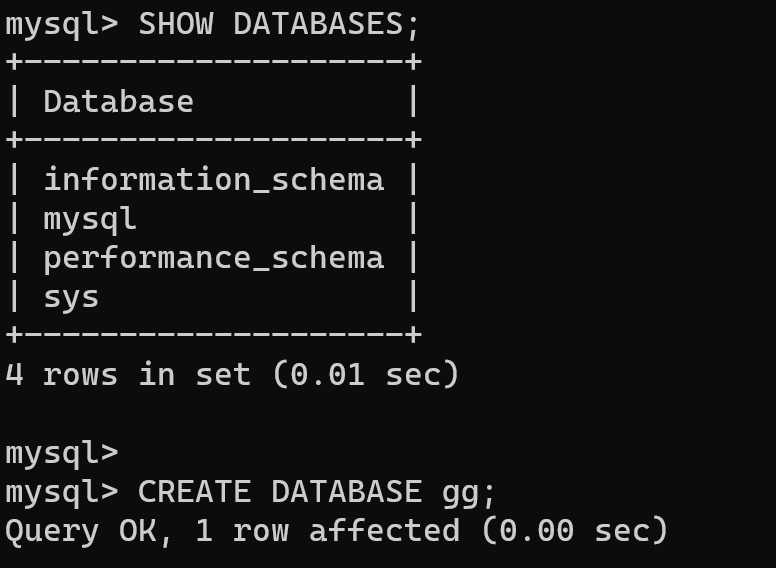
After creation database we need to prepare data, by the command we can create table and fill row with needed records:
sysbench oltp_read_write --table-size=1000000 --db-driver=mysql --mysql-host=127.0.0.1 --mysql-db=gg - -mysql-user=root --mysql-password=123321 prepare 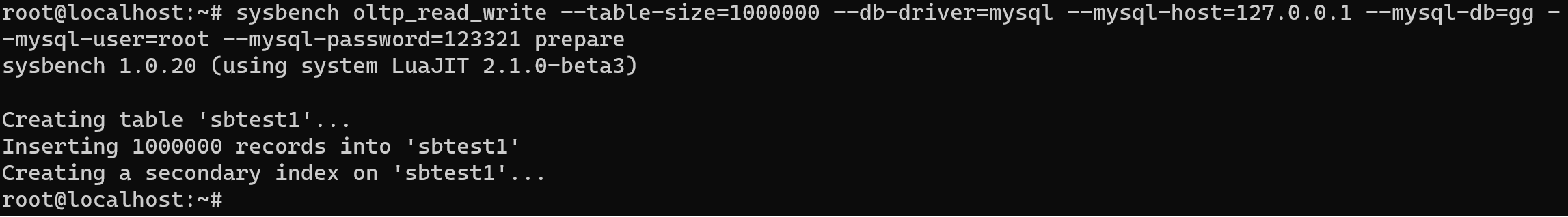
Remember! You need to change credentials for account!
Options table size indicate number of records in the table, user and password are credentials, db-driver using DBMS system for check. Was created table sbtest1. Now we can run the test by the command below:
sysbench oltp_read_write --threads=2 --report-interval=3 --histogram --time=50 --table-size=1000000 --db-driver=mysql --mysql-host=127.0.0.1 --mysql-db=gg - -mysql-user=root --mysql-password=123321 run 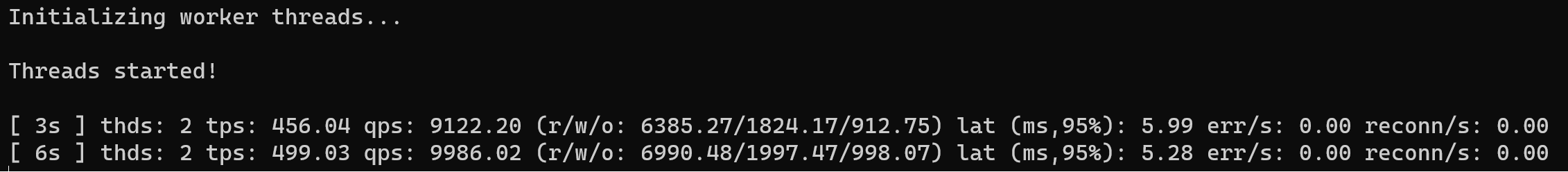
Wait until process will be end. Also one of significant key in the stress testing it's interpreter result. You need to compare output data with theoretical load on the system. Several significant parameters in that report - queries and transaction per second. Our server give pretty good result:
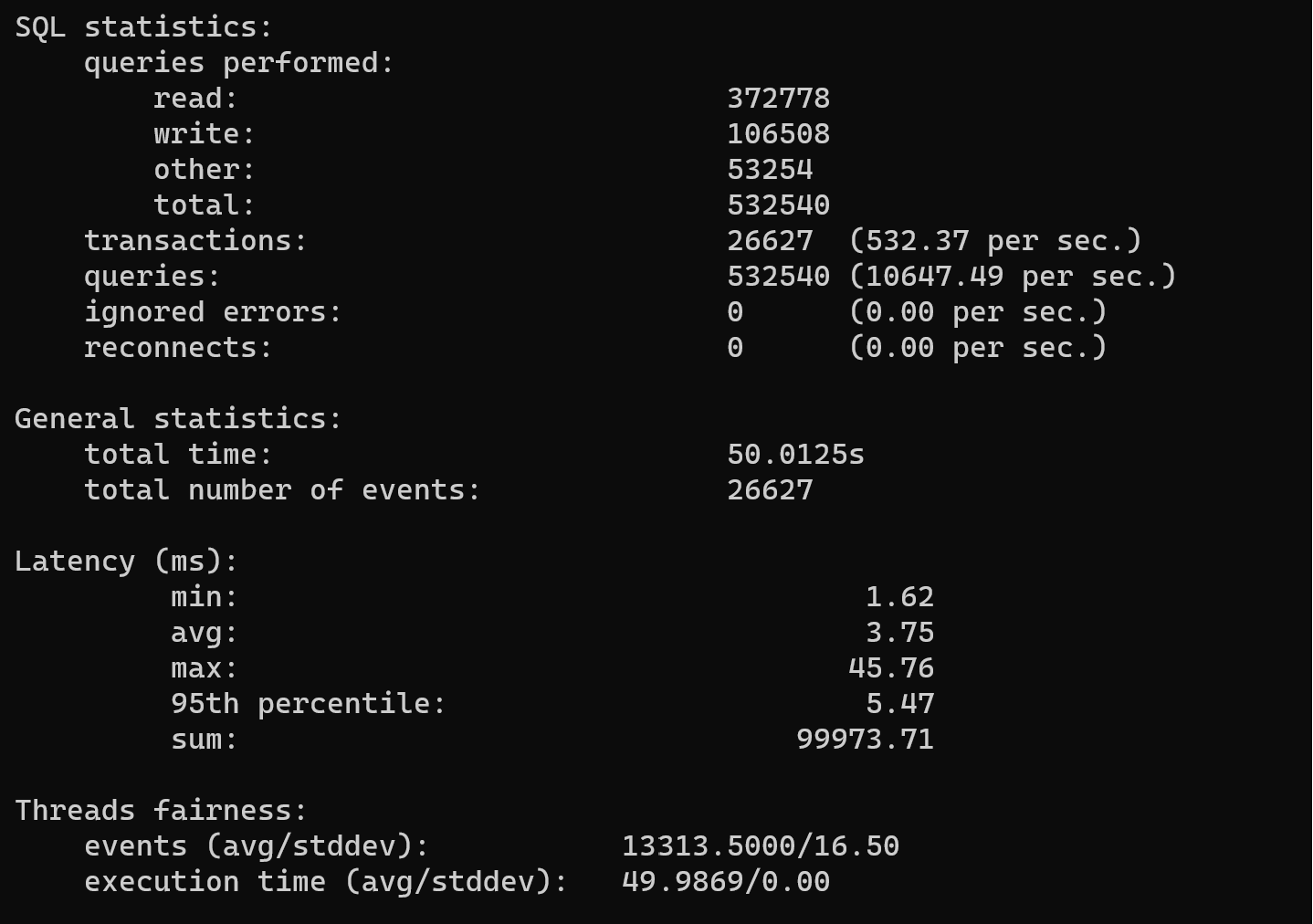
Now, if we don't want to store garbage files, then we need cleanup them by the command:
sysbench oltp_read_write --db-driver=mysql --mysql-host=127.0.0.1 --mysql-db=gg --mysql-user=root --mysql-password=123321 cleanup 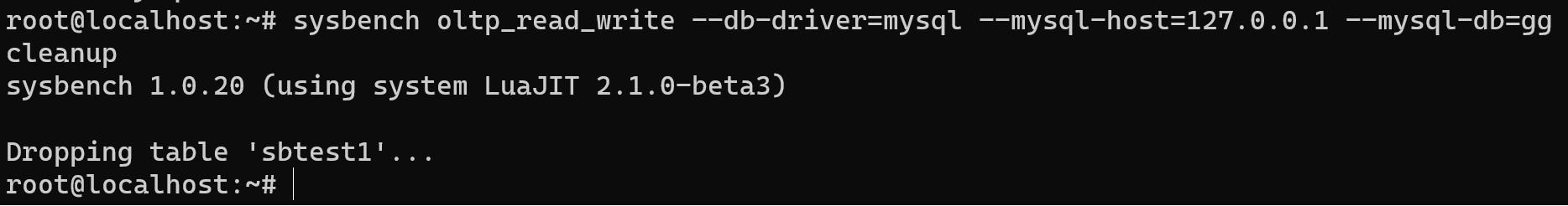
All saved data was dropped and memory was cleaned!
Overall, the provided content outlines a step-by-step process for stress testing a DBMS using sysbench, covering preparation, execution, result interpretation, and cleanup.



