In today’s fast-paced business environment, companies continually face new challenges and complex tasks that demand innovative solutions. However, these challenges often stem from limited specialized resources, tight deadlines, or insufficient oversight by decision-makers. As a result, organizations may implement solutions or systems that are ill-suited to their needs, leading to inefficiencies and missed opportunities. In such situations, lack of clarity and direction can cause further complications, ultimately jeopardizing the success of critical initiatives.
To overcome these challenges, automation and outsourcing cloud platforms are becoming increasingly popular as they provide fault-tolerance, horizontal scalability, and ease of control for system solutions. One such service is Serverspace: Object Storage — SWIFT, which provides a highly structured system that can contain data within containers using its method or metadata. In contrast to traditional file servers or cloud storage, SWIFT offers several advantages, including the ability to store large amounts of unstructured data and easily search for it later on.
Setup CLI
To begin, let us update our indexes and packages first. We will utilize the yum packet manager for Oracle:
yum update -y
Following the update of indexes and packages, the next step is to install the Python package manager, through which we can search for and download the client utility that allows us to manage our storage:
yum install python3-pip
Obviously, next step will be download API client on the system:
pip3 install python-swiftclient python-keystoneclient 
Typically, many Linux distributions come with the packages already installed; however, keeping them up to date is crucial. If Python and pip3 are already installed but pip3 cannot be found, we can utilize the following command to enable the package manager for Python.
python -m ensurepip --default-pipIn case the previous solution does not resolve the issue, we may need to remove any existing versions of Python and pip3 before attempting a fresh installation. Alternatively, we could try updating the currently installed packages.
yum reinstall python3-pipThese steps should help us resolve any issues encountered and provide the necessary tools to manage our storage.
Configuration and Usage
To proceed with ordering Swift Storage from Serverspace, log in to your account and navigate to the Storage section on the left-hand side of the page. If you have already ordered Swift Storage, feel free to skip this step:
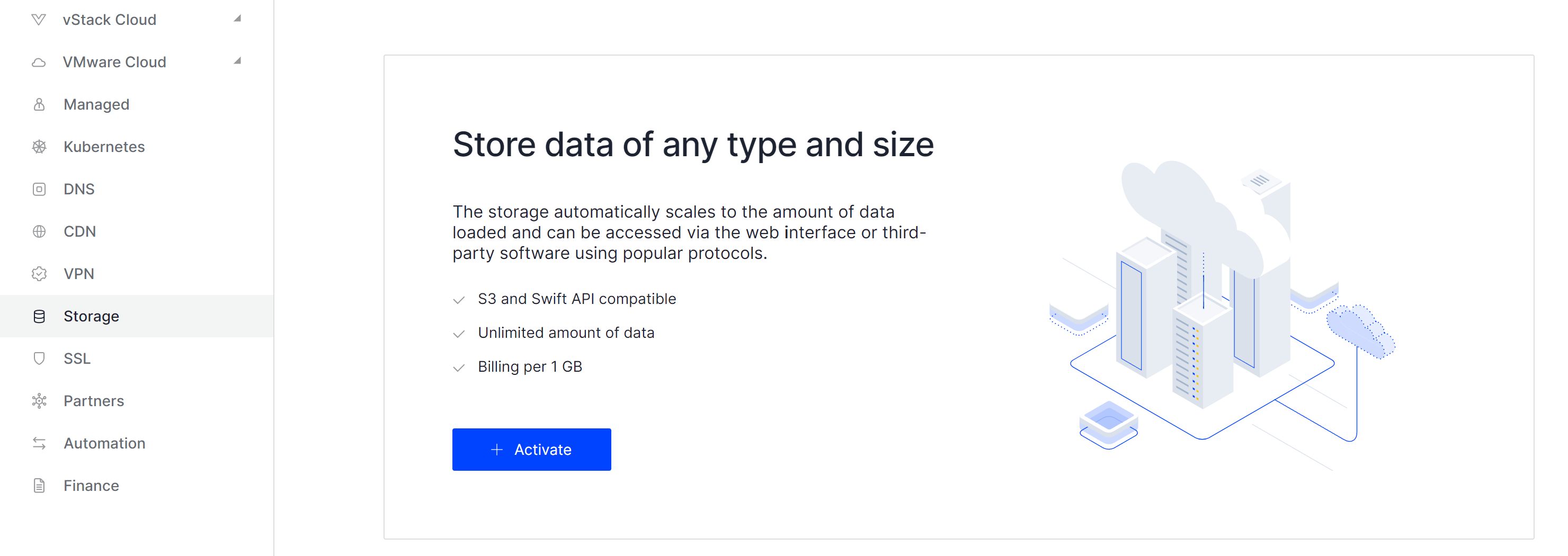
Once you find the Activate button centered on the screen, click it and allow a few seconds for the deployment process to begin. You will now be able to access the main management interface for your Swift Storage:
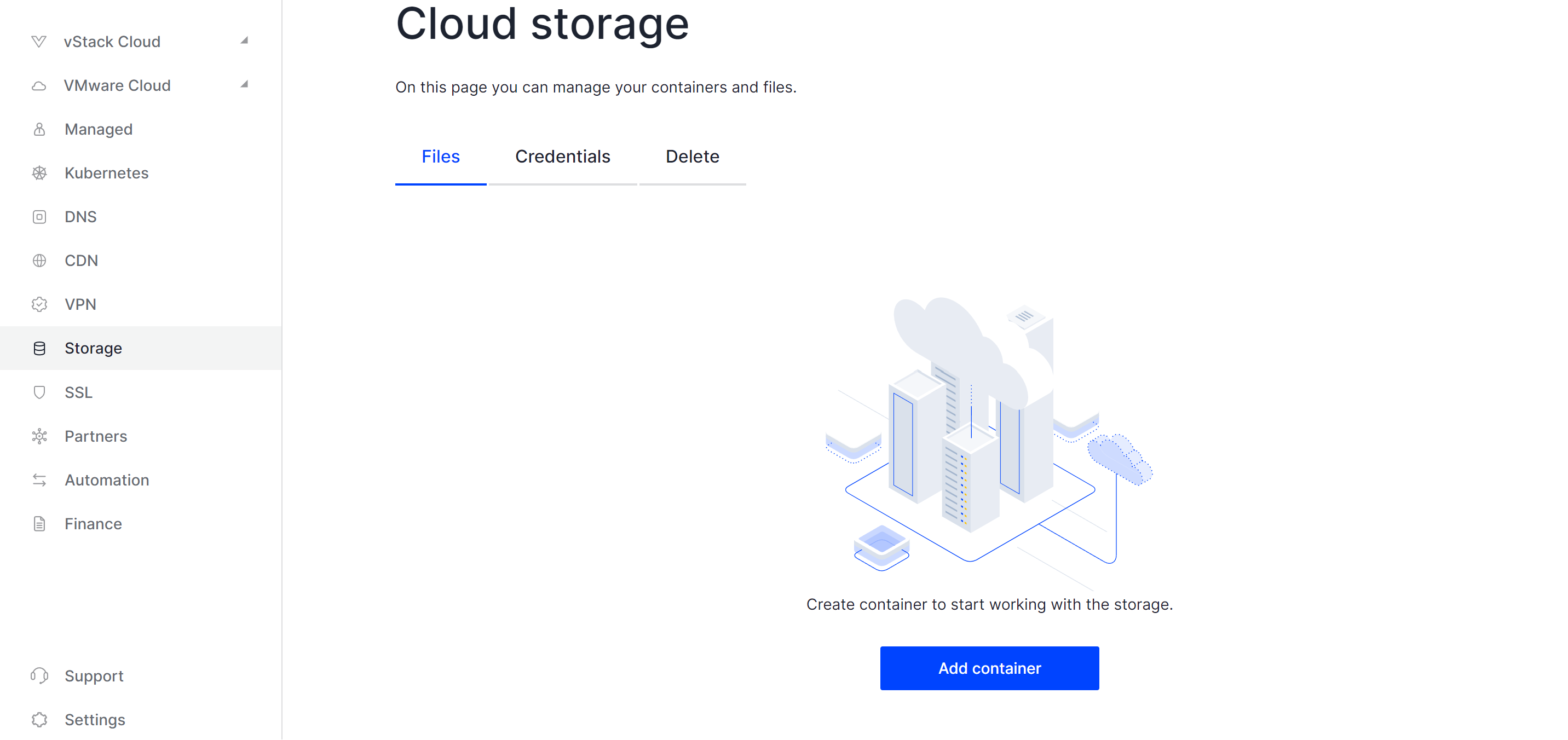
Of course, you can manage your data using a web interface for personal use, which may be more convenient. However, when dealing with corporate networks, automation is often necessary. To begin, press the Add Container button and provide it with a name. After that, upload a file to test the connection further:
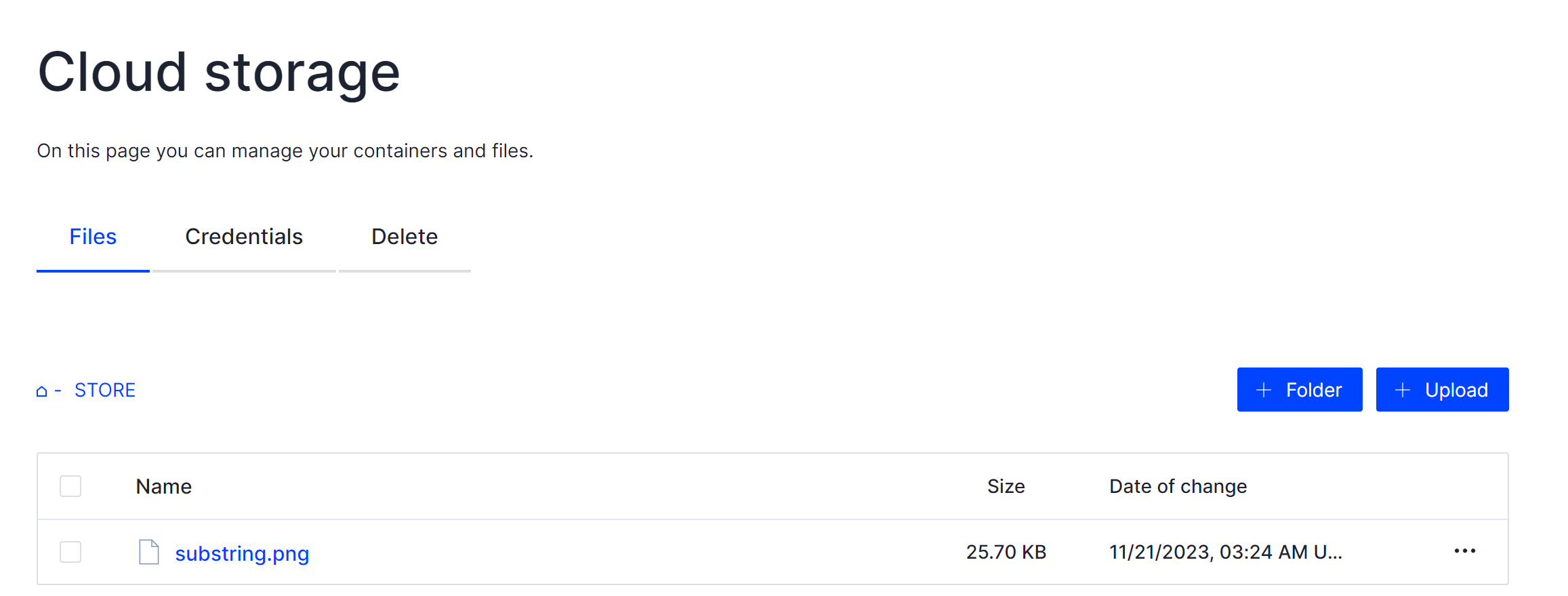
Please locate the Tab labeled Credentials on your screen, then click on it to access the section pertaining to Swift connections:
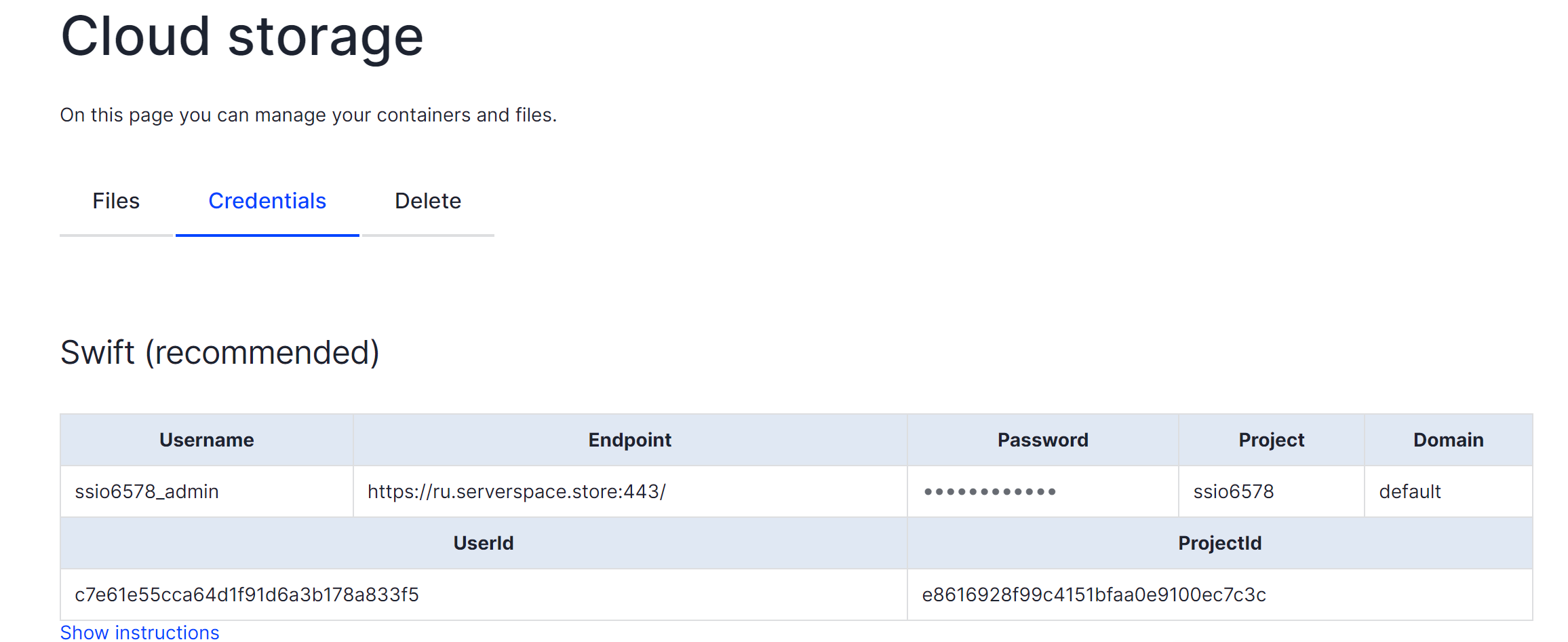
For the time being, kindly keep this information handy. Next, please access the device that contains the downloaded client software. Once there, locate the command prompt and input your credentials as displayed in the table. This will enable us to establish a connection with SWIFT storage and manipulate data:
swift \
--os-storage-url $(Endpoint)/v1/AUTH_$(UserID) \
--os-password $(Password) \
--os-username $(Username) \
--os-project-name $(Project) \
--os-project-domain-name $(Domain) \
--os-auth-url $(Endpoint) \
stat -vIn our case, command will look like this:
swift --os-storage-url https://ru.serverspace.store:443/v1/AUTH_c7e61e55cca64d1f91d6a3b178a833f5 --os-password 6bfa1hdD2Dzr --os-username ssio6578_admin --os-project-name ssio6578 --os-project-domain-name default --os-auth-url https://ru.serverspace.store:443/ download STORE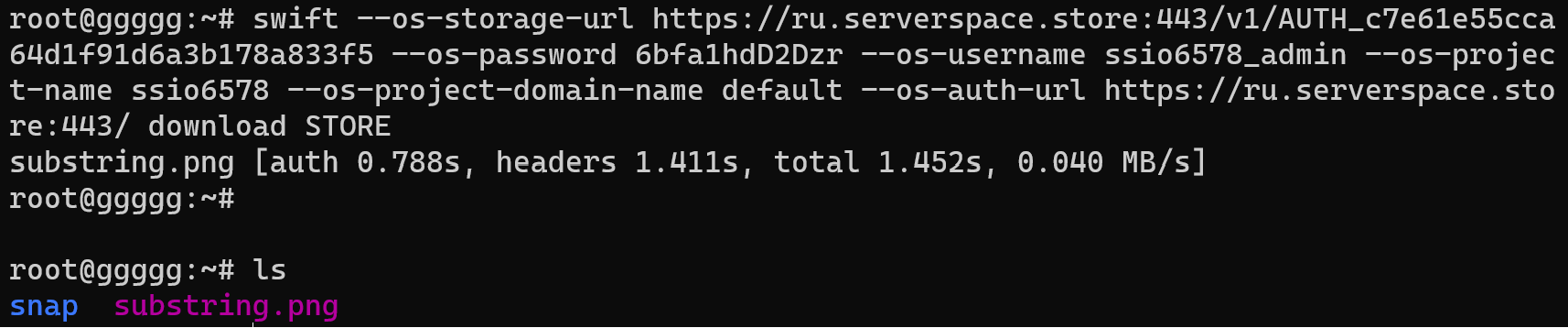
Observe that this command is a request to the API for retrieving data from storage, utilizing your provided credentials. To verify the downloaded information, you may employ the following command:
lsTo streamline the authentication process and manage access to your storage, consider creating an alias entry within your user login script:
echo "alias swift_request='swift --os-storage-url https://ru.serverspace.store:443/v1/AUTH_c7e61e55cca64d1f91d6a3b178a833f5 --os-password 6bfa1hdD2Dzr --os-username ssio6578_admin --os-project-name ssio6578 --os-project-domain-name default --os-auth-url https://ru.serverspace.store:443/'" >> ~/.bashrc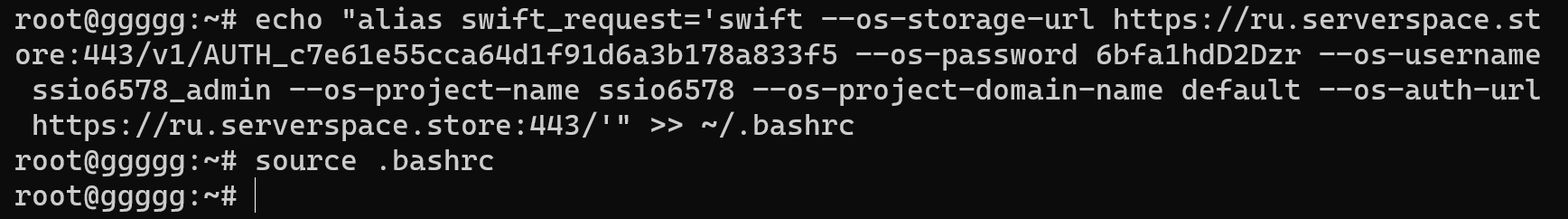
You may choose a descriptive name for this request, such as swift_request. In case your login credentials have been updated (e.g., following a storage reactivation or other reasons), you can modify them in the .bashrc file by executing the command provided below:
nano ~/.bashrcNecessarily! You have to save entering alias by the command:
source .bashrcTo ensure proper function, kindly remove any unnecessary files associated with the storage container:
swift_request delete STORE
By executing the swift_request alias, you will initiate a sequence of commands defined within the corresponding script. Following this, you can append additional parameters to the request as needed.
Conclusion
In summary, this tutorial provides a comprehensive guide on connecting to Oracle Object Storage using the SWIFT CLI. It highlights the value of a structured approach and showcases how leveraging automation and cloud services can significantly boost operational efficiency. By following the detailed steps in this guide, you will develop a solid understanding of the connection process and be fully prepared to implement it effectively in your environment.



