Working with disc space is one of the key skills in OS administration. It often happens that the size of a disc partition may be insufficient for services, in such cases it is expanded by reducing the size of others. The LVM tool allows dynamic resizing without rebooting the device.
How to quickly reduce partition size?
If you don't have sufficient resources than you can perform actions on powerful cloud servers. Serverspace provides isolated VPS / VDS servers for common and virtualize usage.
First of all it is necessary to install a set of tools that will be used to partition the disc space. To work with the physical disc and its logical partitions we need the parted utility, and to work with lvm we need the lvm2 utility:
apt update && apt install parted lvm2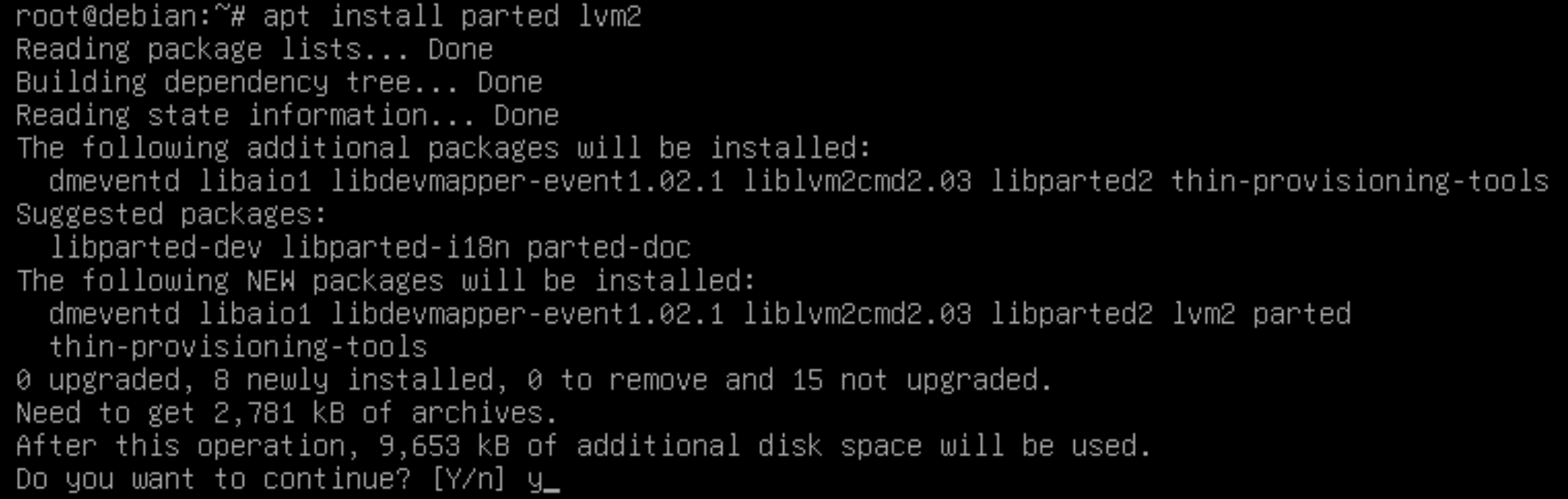
Great, now that we have all the tools from the toolbox - let's go through the list of mounted file systems:
df -H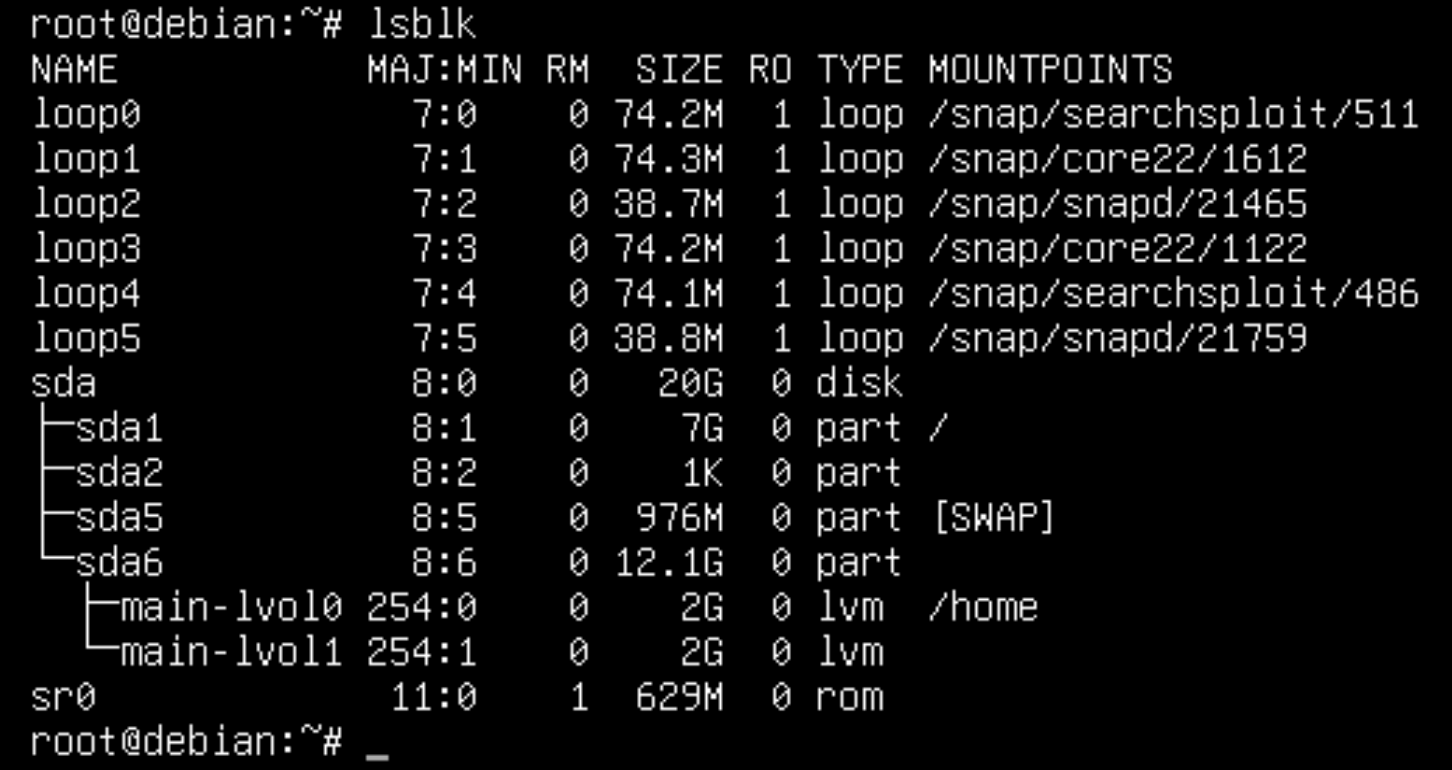
When installing the image in /home, we lacked 2 GB - we need to increase the size to 3 GB, at the expense of the second partition. Unmount the working partition with the command:
umount /dev/main/lvol0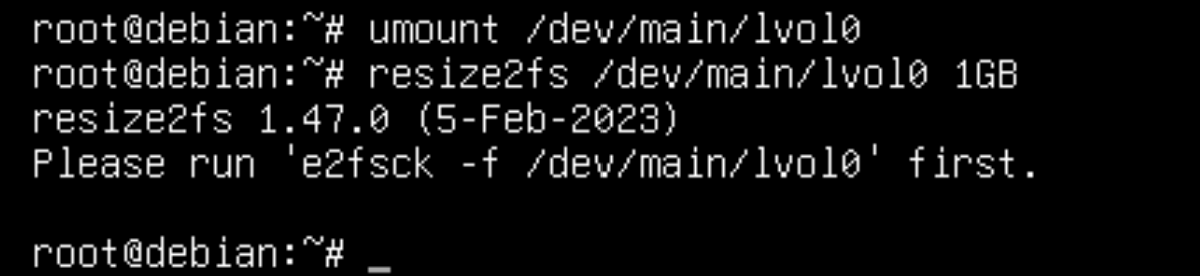
Note that you need to specify your logical partition! After the partition has been unmounted and is not used by the system - we can set a new space size for it.
resize2fs /dev/main/lvol0The warning asks you to scan the partition for errors with the e2fsck utility, after which you will need to repeat the command. Let's speed up the process by entering two commands at once:
e2fsck -f /dev/main/lvol0 && resize2fs /dev/main/lvol0 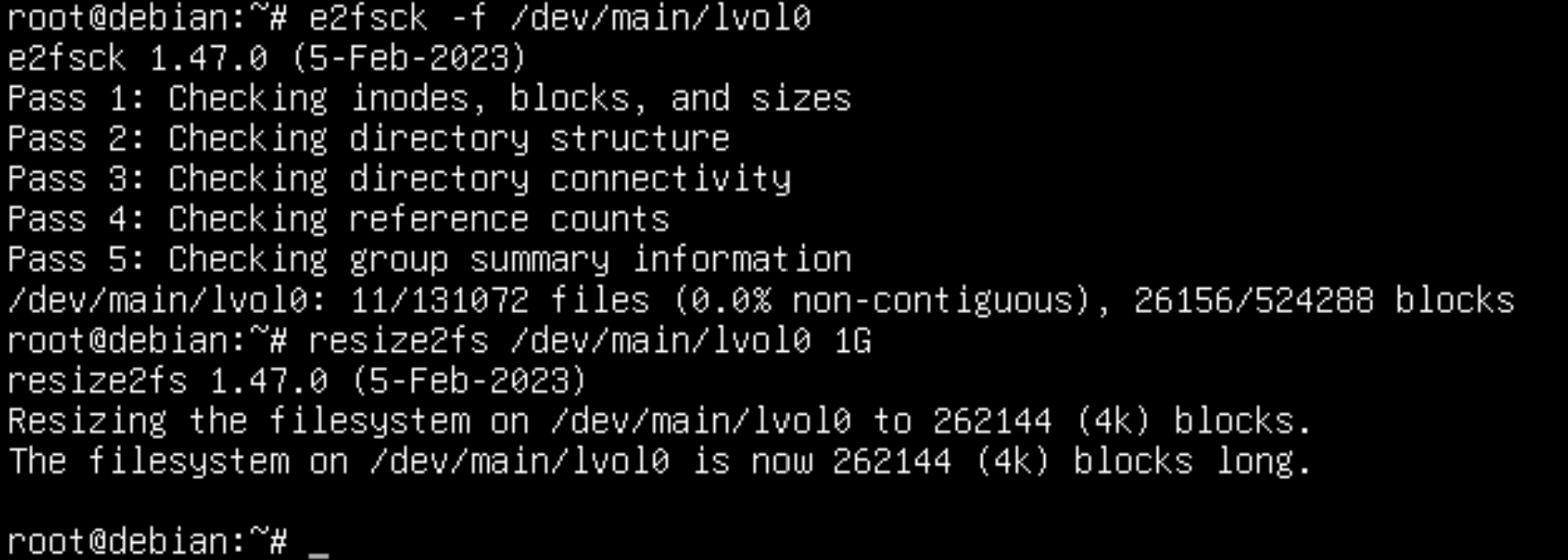 Screenshot №5 — Reduce filesystem
Screenshot №5 — Reduce filesystem
Great, the message at the end notifies you of the new FS size. Shrink the lvm system logical partition with the command below:
lvreduce -L 1G /dev/main/lvol0 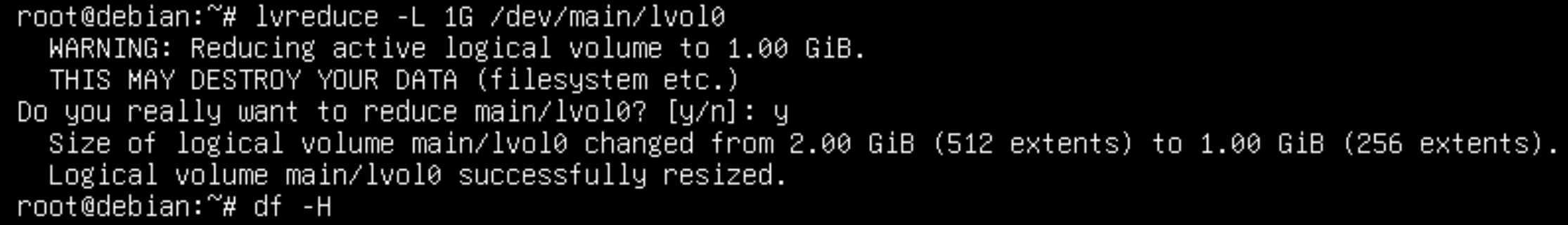
The output of the command shows that the task was successfully completed, the partition was reduced! Using the freed space, we will enlarge another logical partition. Don't forget to mount partitions!
How to quickly increase the partition size?
Now the free space of the virtual group is exactly 1 GB, it must be defined to the logical partition lvol1. To do this, we will proceed in reverse order, first increasing the volume size:
lvextend -L /dev/main/lvol1 3GYou can find your volume with the lvscan command, in case it is not shown via df -H. After that let's increase the file system size to the maximum available:
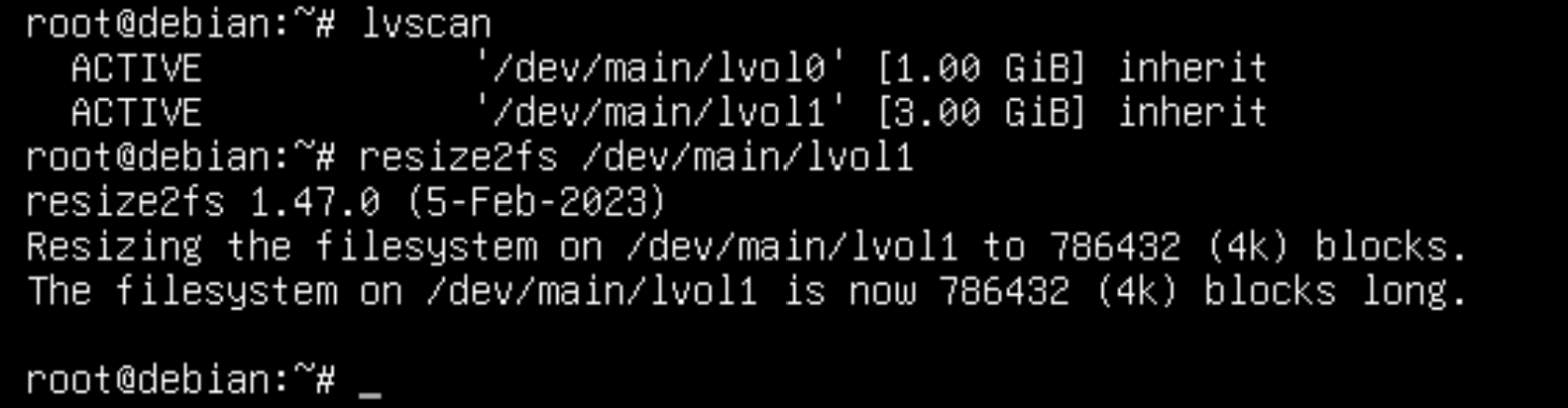
In a few commands the space was enlarged and moved from the neighbouring partition, all that was left was to mount it and test it to see if it worked:
mount /dev/main/lvol1 && df -H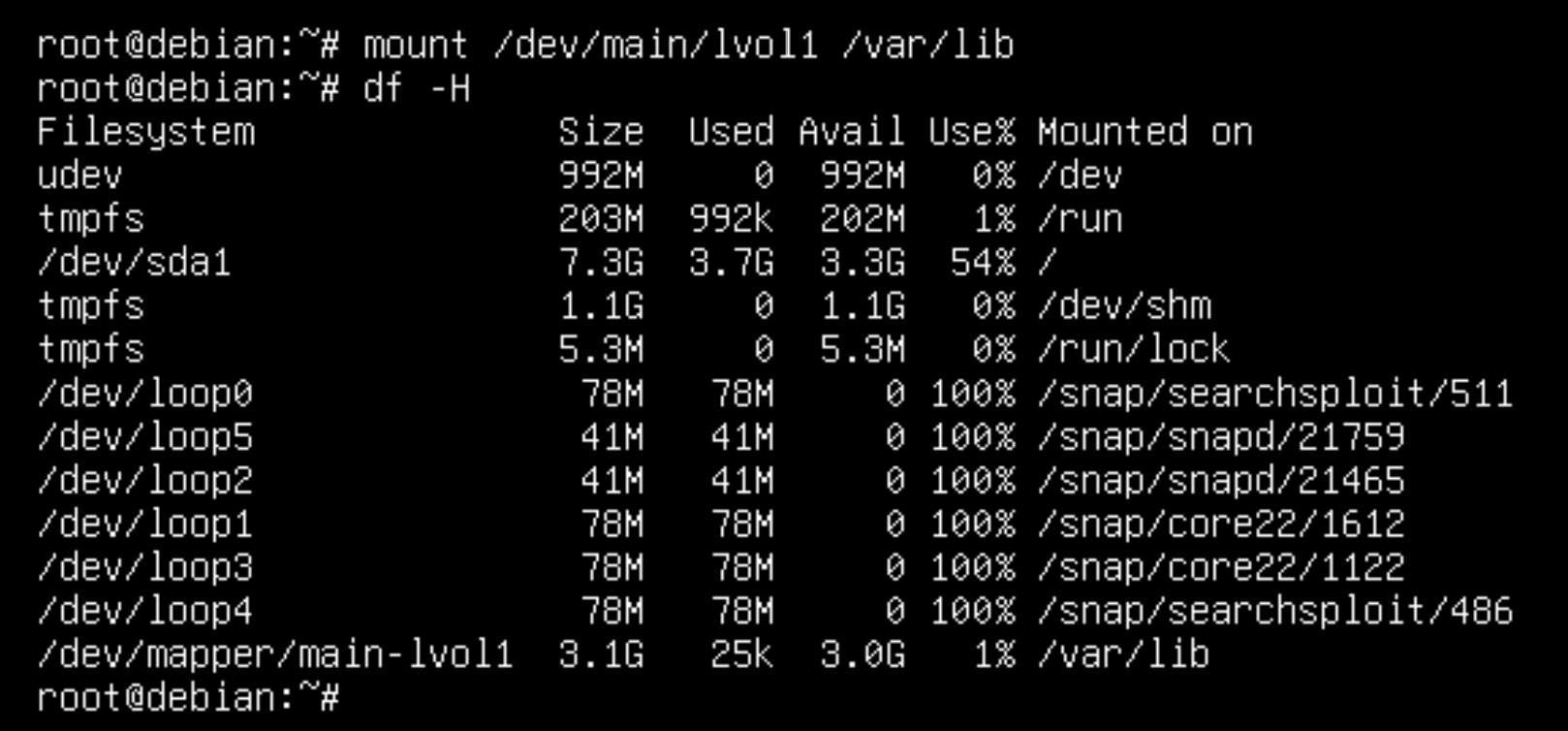
FAQ
- 1. What is LVM and why should I use it?
LVM (Logical Volume Manager) is a tool that allows flexible disk management in Linux. Unlike static partitions, LVM makes it possible to resize, move, and extend volumes without rebooting the system, which is especially useful in production environments. - 2. Can I reduce and increase partition sizes without data loss?
Yes, but you must be careful. Always unmount the partition before resizing and run e2fsck to check for errors. Even though LVM supports resizing, it’s strongly recommended to create backups before making changes. - 3. What tools do I need to work with partitions in Linux?
You’ll need:
parted - for working with physical disks and partitions.
lvm2 - for managing logical volumes under LVM.
e2fsck and resize2fs - for checking and resizing file systems. - 4. How do I quickly reduce a partition size?
Unmount the partition, run e2fsck, and then use resize2fs followed by lvreduce. This frees up space that can be assigned to another logical volume. - 5. How do I extend a partition size?
First, extend the logical volume with lvextend, then resize the file system with resize2fs. Afterward, mount the partition and verify the changes with df -H. - 6. Is it safe to perform these operations on a live server?
Yes, but only if done carefully. Since resizing operations can be risky, test them on a non-critical system first or use cloud solutions such as VPS/VDS to practice. - 7. What if my partition doesn’t show up in df -H?
Use lvscan to list all logical volumes. This command helps you identify hidden or unmounted volumes before resizing them. - 8. Can these operations be performed on cloud servers?
Yes, cloud providers like Serverspace offer VPS/VDS servers that support LVM, making it possible to dynamically adjust storage resources without downtime.



