Working with infrastructure often requires additional tools and utilities to help with trabshooting and solving network and service configuration tasks, one such tool is nslookup!
In this article we will look at what it is and why it is used in the process of checking configurations and network connections.э
What is nslookup?
Nslookup is a DNS troubleshooting utility that allows you to get IP addresses from domain names and vice versa using server records.
For example, typically a server has a list of different records for its gg[.]com domain:
- A record of type A, which refers to the same domain;
- A record of type MX, which points to mail of that domain;
- A record of type TXT, which contains the DKIM public key;
- A record of type PTR, which contains information about the domain by IP address.
And the utility, having addressed with a request, where the record type and domain will be specified, will receive a reply with the address or other requested information.
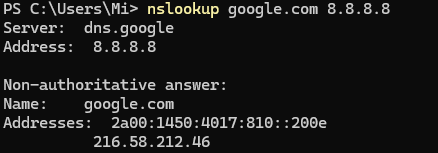
On Windows, nslookup is installed, by default, and can be invoked via Win+X → Terminal/PowerShell:
nslookup /help For Linux, you can use a similar dig utility by first installing a package with it:
apt install net-tools -y && dig --help How do I use nslookup?
The syntax of the utility itself is a classic set of passed options and arguments:
nslookup -[options] host server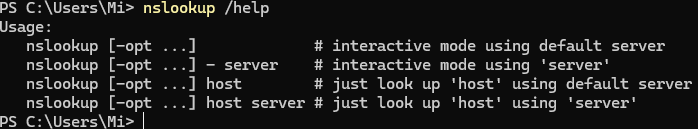
Where nslookup is the command to invoke the utility, -opt options, host is the requested resource on the resolv or mapping, and server is the DNS server to which the resolv request will go. The options can be as follows.
To view the address that the domain is referencing you can command:
nslookup -type A google.com Or specify a different DNS-server for it, this can be useful when testing external and internal service:
nslookup -type A google.com 8.8.8.8.8-type=<type> Specifies the type of DNS record you want to query:
A - address (IPv4);
AAAA - address (IPv6);
CNAME - canonical name;
MX - mail server;
NS - name server records;
PTR - reverse records;
SOA - initial zone entry;
TXT - text records.
If the DNS service uses a non-standard port, it can be accessed with the custom option:
nslookup -port=5156 google.com When the network connection is not the fastest, you may need to increase the response time:
nslookup -timeout=10 google.comTo see the details of the response, use the -debug option, and to increase the number of attempts, specify them directly:
nslookup -retry=3 -debug example.comSuch a solution will be of great help when checking the configuration of DNS-server or paths accessed by the device. For example, if the gg.com site does not open, the answer to the nslookup request says that the ip address is 192.168.1.1, which is not accessible to the device! Thus you can trabshooting on interaction of DNS-server and devices in the network!
As a result of executing these commands you should get a list of parameters of the requested objects. If you don't have sufficient resources than you can perform actions on powerful cloud servers. Serverspace provides isolated VPS / VDS servers for common and virtualize usage.
Conclusion
Nslookup is a powerful DNS troubleshooting utility that helps administrators and users query DNS records and verify network configurations. By using nslookup, you can quickly retrieve IP addresses from domain names, check mail servers, canonical names, text records, and more. Whether testing internal or external DNS servers, nslookup provides essential insights into DNS resolution, allowing you to identify misconfigurations, connectivity issues, or incorrect mappings efficiently. This makes it an invaluable tool for network troubleshooting and system administration.
FAQ
- Q1: What is nslookup used for?
A: Nslookup is used to query DNS servers and retrieve information about domain names, IP addresses, mail servers, and other DNS records. It helps troubleshoot DNS resolution issues. - Q2: Is nslookup available on all operating systems?
A: Yes. Nslookup comes pre-installed on Windows. On Linux, you can use nslookup or install dig via apt install net-tools for similar functionality. - Q3: How do I check a domain's IP address using nslookup?
A: Use the command:nslookup -type=A example.comThis will return the IPv4 address associated with the domain.
- Q4: Can I specify a custom DNS server in nslookup?
A: Yes. You can query a specific DNS server by adding it at the end of the command:
nslookup -type=A example.com 8.8.8.8 - Q5: How do I query different types of DNS records?
A: Use the -type option to specify the record type:
A – IPv4 address
AAAA – IPv6 address
MX – mail server
CNAME – canonical name
NS – name server
PTR – reverse DNS
TXT – text records - Q6: How can I debug slow or failing DNS responses?
A: Use options like -timeout, -retry, and -debug to increase response time, retry attempts, and see detailed output:nslookup -timeout=10 -retry=3 -debug example.com



